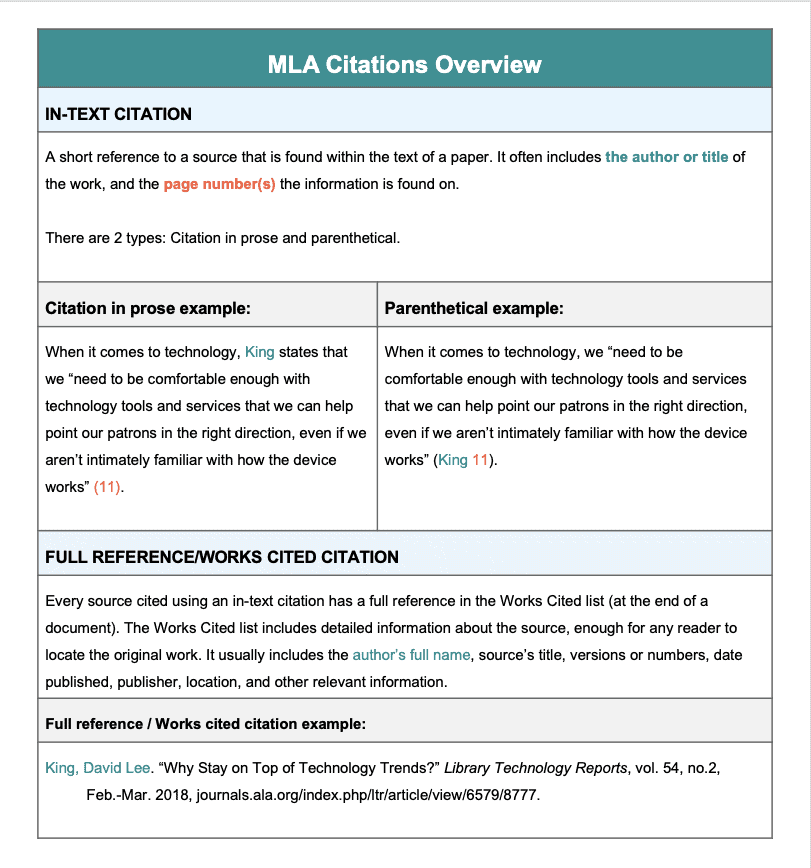
An in-text citation is a reference to a source that is found within the text of a paper (Handbook 227). This tells a reader that an idea, quote, or paraphrase originated from a source. MLA in-text citations usually include the last name of the author and the location of cited information.
This guide focuses on how to create MLA in-text citations, such as citations in prose and parenthetical citations in the current MLA style, which is in its 9th edition. This style was created by the Modern Language Association. This guide reviews MLA guidelines but is not related directly to the association.
Here’s a quick rundown of the contents of this guide on how to use in-text citations.
An in-text citation is a general citation of where presented information came from. In MLA, an in-text citation can be displayed in two different ways:
While the two ways are similar, there are slight differences. However, for both ways, you’ll need to know how to format page numbers in MLA.
An MLA citation in prose is when the author’s name is used in the text of the sentence. At the end of the sentence, in parentheses, is the page number where the information was found.
When it comes to technology, King states that we “need to be comfortable enough with technology tools and services that we can help point our patrons in the right direction, even if we aren’t intimately familiar with how the device works” (11).
This MLA citation in prose includes King’s name in the sentence itself, and this specific line of text was taken from page 11 of the journal it was found in.
An MLA parenthetical citation is created when the author’s name is NOT in the sentence. Instead, the author’s name is in parentheses after the sentence, along with the page number.
When it comes to technology, we “need to be comfortable enough with technology tools and services that we can help point our patrons in the right direction, even if we aren’t intimately familiar with how the device works” (King 11).
In the above example, King’s name is not included in the sentence itself, so his name is in parentheses after the sentence, with 11 for the page number. The 11 indicates that the quote is found on page 11 in the journal.
For every source that is cited using an in-text citation, there is a corresponding full reference. This allows readers to track down the original source.
At the end of the assignment, on the MLA works cited page, is the full reference. The full reference includes the full name of the author, the title of the article, the title of the journal, the volume and issue number, the date the journal was published, and the URL where the article was found.
King, David Lee. “Why Stay on Top of Technology Trends?” Library Technology Reports, vol. 54, no. 2, Feb.-Mar. 2018, ezproxy.nypl.org/login?url=//search-proquest-com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/docview/2008817033?accountid=35635.
Readers can locate the article online via the information included above.

The next section of this guide focuses on how to structure an MLA in-text citation and reference in parentheses in various situations.
A narrative APA in-text citation and APA parenthetical citation are somewhat similar but have some minor differences. Check out our helpful guides, and others, on EasyBib.com!
Wondering how to handle these types of references in other styles? Check out our page on APA format, or choose from more styles.
| Author/Sources | In-text citation | Structure & Explanation |
|---|---|---|
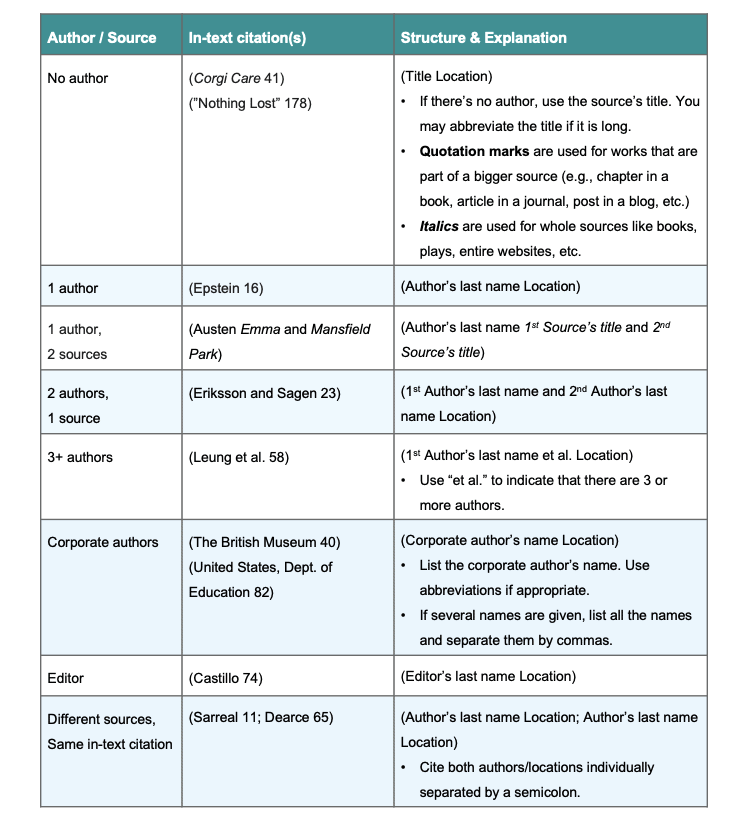
| No author | (Corgi Care 41) |
Use the title. Use an abbreviated version if it’s long. Format the title like you do in the reference.
“Quotation marks” = Work that’s part of a bigger source (e.g., book chapter, journal article, blog post, etc.)
There are many books, journal articles, magazine articles, reports, and other source types written or created by two authors.
When a source has two authors, place both authors’ last names in the body of your work (Handbook 232). The last names do not need to be listed in alphabetical order. Instead, follow the same order as shown on the source.
In an MLA in-text citation, separate the two last names with the word “and.” After both authors’ names, add a space and the page number where the original quote or information is found on.
Gaiman and Pratchett further elaborate by sharing their creepy reminder that “just because it’s a mild night doesn’t mean that dark forces aren’t abroad. They’re abroad all of the time. They’re everywhere” (15).
Don’t forget that “just because it’s a mild night doesn’t mean that dark forces aren’t abroad. They’re abroad all of the time. They’re everywhere” (Gaiman and Pratchett 15).
If you’re still confused, check out EasyBib.com’s MLA in-text citation generator, which allows you to create MLA in-text citations and other types of references in just a few clicks!
If it’s an APA book citation you’re looking to create, we have a helpful guide on EasyBib.com. While you’re at it, check out our APA journal guide!
There are a number of sources written or created by three or more authors. Many research studies and reports, scholarly journal articles, and government publications are developed by three or more individuals.
If you included the last names of all individuals in your MLA in-text citations or in parentheses, it would be too distracting to the reader. It may also cause the reader to lose sight of the overall message of the paper or assignment. Instead of including all last names, only include the last name of the first individual shown on the source. Follow the first author’s last name with the Latin phrase, “et al.” This Latin phrase translates to “and others.” Add the page number after et al.
“School library programs in Croatia and Hong Kong are mainly focused on two major educational tasks. One task is enhancing students’ general literacy and developing reading habits, whereas the other task is developing students’ information literacy and research abilities” (Tam et al. 299).
The example above only includes the first listed author’s last name. All other authors are credited when “et al.” is used. If the reader wants to see the other authors’ full names, the reader can refer to the final references at the end of the assignment or to the full source.
The abbreviation et al. is used with references in parentheses, as well as in full references. To include the authors’ names in prose, you can either write each name out individually or, you can type out the meaning of et al., which is “and others.”
School library programming in Croatia and Hong Kong is somewhat similar to programming in the United States. Tam, Choi, Tkalcevic, Dukic, and Zheng share that “school library programs in Croatia and Hong Kong are mainly focused on two major educational tasks. One task is enhancing students’ general literacy and developing reading habits, whereas the other task is developing students’ information literacy and research abilities” (299).
If your instructor’s examples of how to do MLA in-text citations for three or more authors looks different than the example here, your instructor may be using an older edition of this style. To discover more about previous editions, learn more here.
Need some inspiration for your research project? Trying to figure out the perfect topic? Check out our Dr. Seuss, Marilyn Monroe, and Malcolm X topic guides!
It may seem unlikely, but there are times when an author’s name isn’t included on a source. Many digital images, films and videos, encyclopedia articles, dictionary entries, web pages, and more do not have author names listed.
If the source you’re attempting to cite does not have an author’s name listed, the MLA in-text citation or parenthetical citation should display the title. If the title is rather long, it is acceptable to shorten it in the body of your assignment. If you choose to shorten the title, make sure the first word in the full citation is also the first word used in the citation in prose or parenthetical citation. This is done to allow the reader to easily locate the full citation that corresponds with the reference in the text.
If, in the Works Cited list, the full reference has the title within quotation marks, include those quotation marks in the in-text citation or reference in parentheses. If the title is written in italics in the full reference, use italics for the title in the in-text citation or reference in parentheses as well.
“From the moment you hold your baby in your arms you will never be the same. You might long for the person you were before, when you had freedom and time and nothing in particular to worry about” (“The Last Time”).
“Perhaps it would have been different if there hadn’t been a war, but this was 1917, and people were exhausted by loss. Those that were allowed to stay manned the pits, mining the coal that would fuel the ships. Twenty-four hours a day they labored” (Englishman).
Notice the shortened title in the above reference. This allows the reader to spend more time focusing on the content of your project, rather than the sources.
If you’re looking for an MLA in-text citation website to help you with your references, check out EasyBib Plus on EasyBib.com! EasyBib Plus can help you determine how to do in-text citations MLA and many other types of references!
Numerous government publications, research reports, and brochures state the name of the organization as the author responsible for publishing it.
When the author is a corporate entity or organization, this information is included in the MLA citation in prose or parenthetical citation.
“One project became the first to evaluate how e-prescribing standards work in certain long-term care settings and assessed the impact of e-prescribing on the workflow among prescribers, nurses, the pharmacies, and payers” (Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 2).
If the full name of the organization or governmental agency is long in length, it is acceptable to abbreviate some words, as long as they are considered common abbreviations. These abbreviations should only be in the references with parentheses. They should not be used in citations in prose.
Here is a list of words that can be abbreviated in parentheses:
“Based on our analysis of available data provided by selected states’ departments of corrections, the most common crimes committed by inmates with serious mental illness varied from state to state” (US Govt. Accountability Office 14).
The United States Government Accountability Office states, “Based on our analysis of available data provided by selected states’ departments of corrections, the most common crimes committed by inmates with serious mental illness varied from state to state” (14).
Remember, citations in prose should not have abbreviations; other types of references can.
Looking for more information on abbreviations? Check out our page on MLA format.
Edited books and anthologies often include chapters or sections, each written by an individual author or a small group of authors. These compilations are placed together by an editor or a group of editors. There are tons of edited books and anthologies available today, ranging from ones showcasing Black history facts and literature to those focusing on notable individuals such as scientists like Albert Eintein and politicians such as Winston Churchill.
If you’re using information from an edited book or an anthology, include the chapter author’s name in your MLA citation in prose or reference in parentheses. Do not use the name(s) of the editor(s). Remember, the purpose of these references is to provide the reader with some insight as to where the information originated. If, after reading your project, the reader would like more information on the sources used, the reader can use the information provided in the full reference, at the very end of the assignment. With that in mind, since the full reference begins with the author of the individual chapter or section, that same information is what should be included in any citations in prose or references in parentheses.
Weinstein further states that “one implication of this widespread adaptation of anthropological methods to historical research was the eclipse of the longstanding concern with “change over time,” and the emergence of a preference for synchronic, rather than diachronic, themes” (195).
Weinstein, Barbara. “History Without a Cause? Grand Narratives, World History, and the Postcolonial Dilemma.” Postcolonial Studies: An Anthology, edited by Pramod K. Nayar, Wiley-Blackwell, 2015, p. 196. Wiley, www.wiley.com/en-us/Postcolonial+Studies%3A+An+Anthology-p-9781118780985.
Once you’re through with writing and citing, run your paper through our innovative plagiarism checker! It’s the editor of your dreams and provides suggestions for improvement.
When a source has no page numbers, which is often the case with long web page articles, e-books, and numerous other source types, do not include any page number information in the body of the project. Do not estimate or invent your own page numbering system for the source. If there aren’t any page numbers, omit this information from the MLA in-text citation. There may, however, be paragraph numbers included in some sources. If there are distinct and clear paragraph numbers directly on the source, replace the page number with this information. Make it clear to the reader that the source is organized by paragraphs by using “par.” before the paragraph number, or use “pars.” if the information is from more than one paragraph.
“She ran through the field with the wind blowing in her hair and a song through the breeze” (Jackson par. 5).
In Brenner’s meeting notes, he further shared his motivation to actively seek out and secure self help resources when he announced, “When we looked at statistical evidence, the most commonly checked out section of the library was self-help. This proves that patrons consistently seek out help for personal issues and wish to solve them with the help of the community’s resources” (pars. 2-3).
Holson writes about a new mindful app, which provides listeners with the soothing sound of not only Bob Ross’ voice, but also the “soothing swish of his painter’s brush on canvas.”
In above example, the information normally found in the parentheses is omitted since there aren’t any page, parentheses, or chapter numbers on the website article.
Looking for APA citation website examples? We have what you need on EasyBib.com!
Need an in-text or parenthetical citation MLA website? Check out EasyBib Plus on EasyBib.com! Also, check out MLA Citation Website, which explains how to create references for websites.
It may seem redundant to constantly include an author’s name in the body of a research project or paper. If you use an author’s work in one section of your project, and the next piece of information included is by the same individual(s), then it is not necessary to share in-text, whether in prose or in parentheses, that both items are from the same author. It is acceptable to include the last name of the author in the first use, and in the second usage, only a page number needs to be included.
“One of the major tests is the Project for Standardized Assessment of Information Literacy Skills. This measurement was developed over four years as a joint partnership between the Association of Research Libraries and Kent State University” (Tong and Moran 290). This exam is just one of many available to measure students’ information literacy skills. It is fee-based, so it is not free, but the results can provide stakeholders, professors, curriculum developers, and even librarians and library service team members with an understanding of students’ abilities and misconceptions.
It is not surprising to read the results, which stated that “upper-level undergraduate students generally lack information literacy skills as evidenced by the results on this specific iteration of the Standardized Assessment of Information Literacy Skills test” (295).
The reader can assume that the information in the second quote is from the same article as the first quote. If, in between the two quotes, a different source is included, Tong and Moran’s names would need to be added again in the last quote.
Tong, Min, and Carrie Moran. “Are Transfer Students Lagging Behind in Information Literacy?” Reference Services Review, vol. 45, no. 2, 2017, pp. 286-297. ProQuest, ezproxy.nypl.org/login?url=//search-proquest-com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/docview/1917280148?accountid=35635.
According to section 6.30 of the Handbook, parenthetical citations containing multiple sources in a single parenthesis should be separated by semicolons.
Just as you might want to cite two different sources at the same time, it can also be useful to cite different works by the same author all at once.
Section 6.30 of the Handbook specifies that “citations of different locations in a single source are separated by commas” (251).
Furthermore, if you are citing multiple works by the same author, the titles should be joined by and if there are only two. Otherwise, use commas and and.
(Murakami, Wild Sheep Chase and Norwegian Wood)
(Murakami, Wild Sheep Chase, Norwegian Wood, and “With the Beatles”)
When listing the titles, be aware that long titles in parenthetical citations can distract the reader and cause confusion. It will be necessary to shorten the titles appropriately for in-text citations. According to the Handbook, “shorten the title if it is longer than a noun phrase” (237). The abbreviated title should begin with the word by which the title is alphabetized.
Best practice is to give the first word the reference is listed by so the source is easily found in the works cited. Omit articles that start a title: a, an, the. When possible, use the first noun (and any adjectives before it). For more on titles and their abbreviations, head to section 6.10 of the Handbook.
There are instances when religious works are italicized in the text of a project, and times when it is not necessary to italicize the title.
If you’re referring to the general religious text, such as the Bible, Torah, or Qur’an, it is not necessary to italicize the name of the scripture in the body of the project. If you’re referring to a specific edition of a religious text, then it is necessary to italicize it, both in text and in the full reference.
Here are some commonly used editions:
When including a reference, do not use page numbers from the scripture. Instead, use the designated chapter numbers and verse numbers.
While, unacceptable in today’s society, the Bible is riddled with individuals who have two, three, and sometimes four or more spouses. One example in the King James Bible, states that an individual “had two wives, the name of the one was Hannah, and the name of the other Peninnah. Peninnah had children, but Hannah had no children” (1 Sam. 1.2)
The only religious scripture that is allowed to be in the text of a project, but not in the Works Cited list, is the Qur’an. There is only one version of the Qur’an. It is acceptable to include the name of the Qur’an in the text, along with the specific chapter and verse numbers.
If you’re attempting to create a reference for a religious work, but it’s not considered a “classic” religious book, such as a biography about Mother Teresa, or a book about Muhammed Ali’s conversion, then a reference in the text and also on the final page of the project is necessary.
If you’re creating an APA bibliography, you do not need to create a full reference for classic religious works on an APA reference page.
For another MLA in-text citation website and for more on the Bible and other source types, click here.
Quotes longer than four lines are called, “block quotes.” Block quotes are sometimes necessary when you’re adding a lengthy piece of information into your project. If you’d like to add a large portion of Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream” speech, a lengthy amount of text from a Mark Twain book, or multiple lines from Abraham Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address, a block quote is needed.
MLA block quotes are formatted differently than shorter quotes in the body of a project. Why? The unique formatting signals to the reader that they’re about to read a lengthy quote.
Block quotes are called block quotes because they form their own block of text. They are set apart from the body of a project with different spacing and margins.
Begin the block quote on a new line. The body of the full project should run along the one inch margin, but the block quote should be set in an inch and a half. The entire quote should be along the inch and a half margin.
If there aren’t any quotation marks in the text itself, do not include any in the block quote. This is very different than standard reference rules. In most cases, quotation marks are added around quoted material. For block quotes, since the reader can see that the quoted material sits in its own block, it is not necessary to place quotation marks around it.
Despite Bruchac’s consistent difficult situations at home, basketball kept his mind busy and focused:
When I got off the late bus that afternoon, my grandparents weren’t home. The store was locked and there was a note from Grama on the house door. Doc Magovern had come to the house because Grampa was “having trouble with his blood.” Now they were off to the hospital and I “wasn’t to worry.” This had happened before. Grampa had pernicious anemia and sometimes was very sick. So, naturally, it worried the pants off me. I actually thought about taking my bike down the dreaded 9N the three miles to the Saratoga Hospital. Instead, I did as I knew they wanted. I opened the store and waited for customers. None came, though, and my eye was caught by the basketball stowed away as usual behind the door. I had to do something to take my mind off what was happening to Grampa. I took out the ball and went around the side. (13)
Notice the use of the colon prior to the start of the block quote. Do not use a colon if the block quote is part of the sentence above it.
Despite Bruchac’s consistent difficult situations at home, it was clear that basketball kept his mind busy and focused when he states
When I get off the late bus that afternoon, my grandparents weren’t home…
If two or more paragraphs are included in your block quote, start each paragraph on a new line.
Looking for additional helpful websites? Need another MLA in-text citation website? Check out the style in the news. We also have other handy articles, guides, and posts to help you with your research needs. Here’s one on how to write an MLA annotated bibliography.
Visit our EasyBib Twitter feed to discover more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
If you’re looking for information on styling an APA citation, EasyBib.com has the guides you need!
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated July 5, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.